Spring Cloud Config自动刷新机制
Spring Cloud Config自动刷新的主要流程
目录
Spring Cloud Config的小坑
本文是基于spring-cloud-netflix 1.4.0.RELEASE版本
在做demo时遇到了个不大不小的坑: Spring Cloud Config 的客户端的配置文件不能用”application.yml”而需要改为”bootstrap.yml”,否则即便你所有的参数都配对了,你在使用@Value注入配置时也会抛出Could not resolve placeholder···异常。
关于git
为何spring cloud config会使用git作为存储配置的仓库呢?我想有以下几个考虑点:
- git自带版本控制
- git自带的branch可以用来支持配置中心的多环境(比如dev,test)
- git自带回滚功能
- git除了key:value之外还可以存储文件
但是也由于Git本身没有事件通知机制所以需要依赖mq来通知各个客户端(而且也只是通知说有配置更新,还需要一次网络交互才能获取到新配置)。总而言之使用git可以带来一些便利,但是也增加了架构的复杂度(需要多一个mq中间件,这也是很多人诟病它的一点吧?)
自动刷新配置
流程:
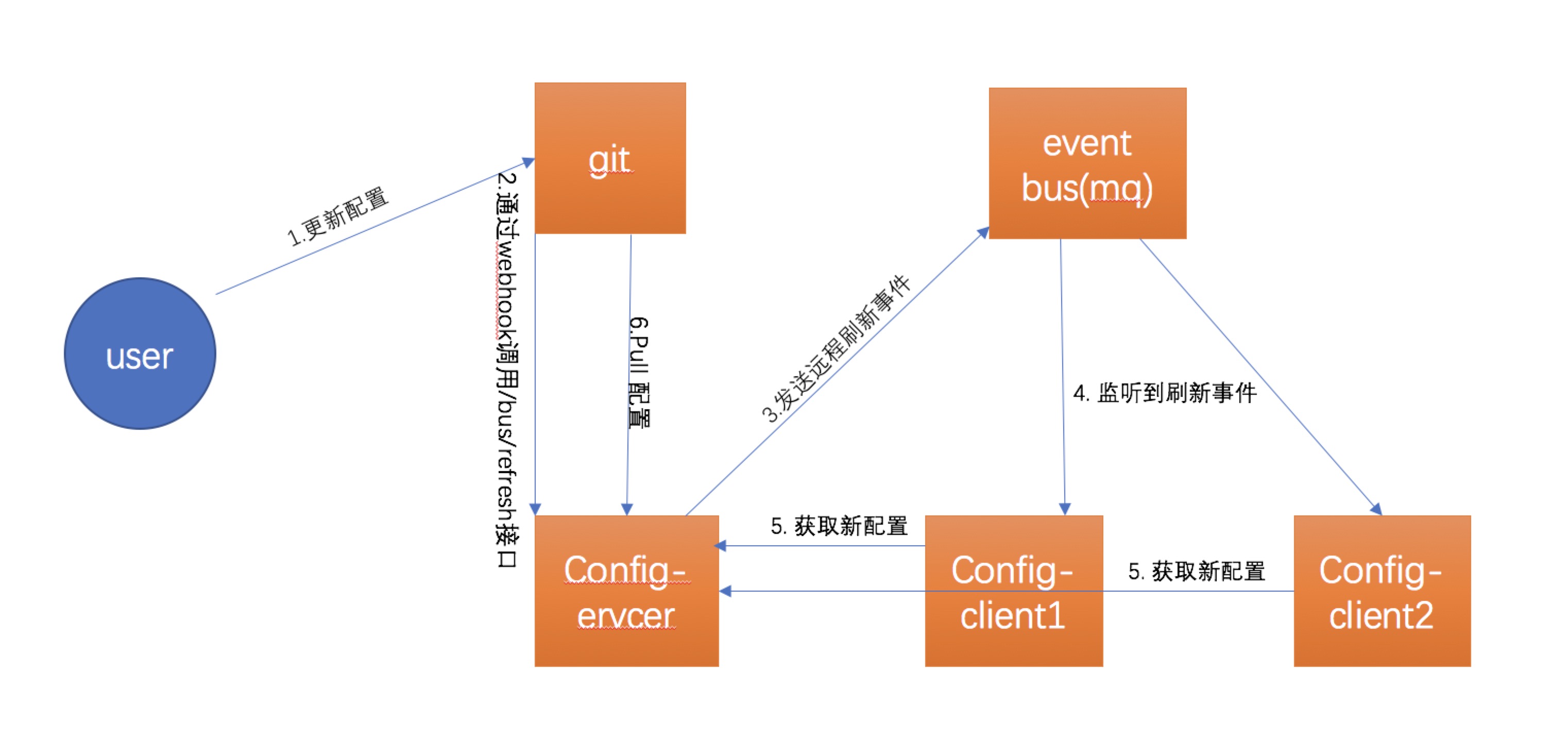
这里是我做的demo,使用了rabbitmq来做消息队列.
源码
config server
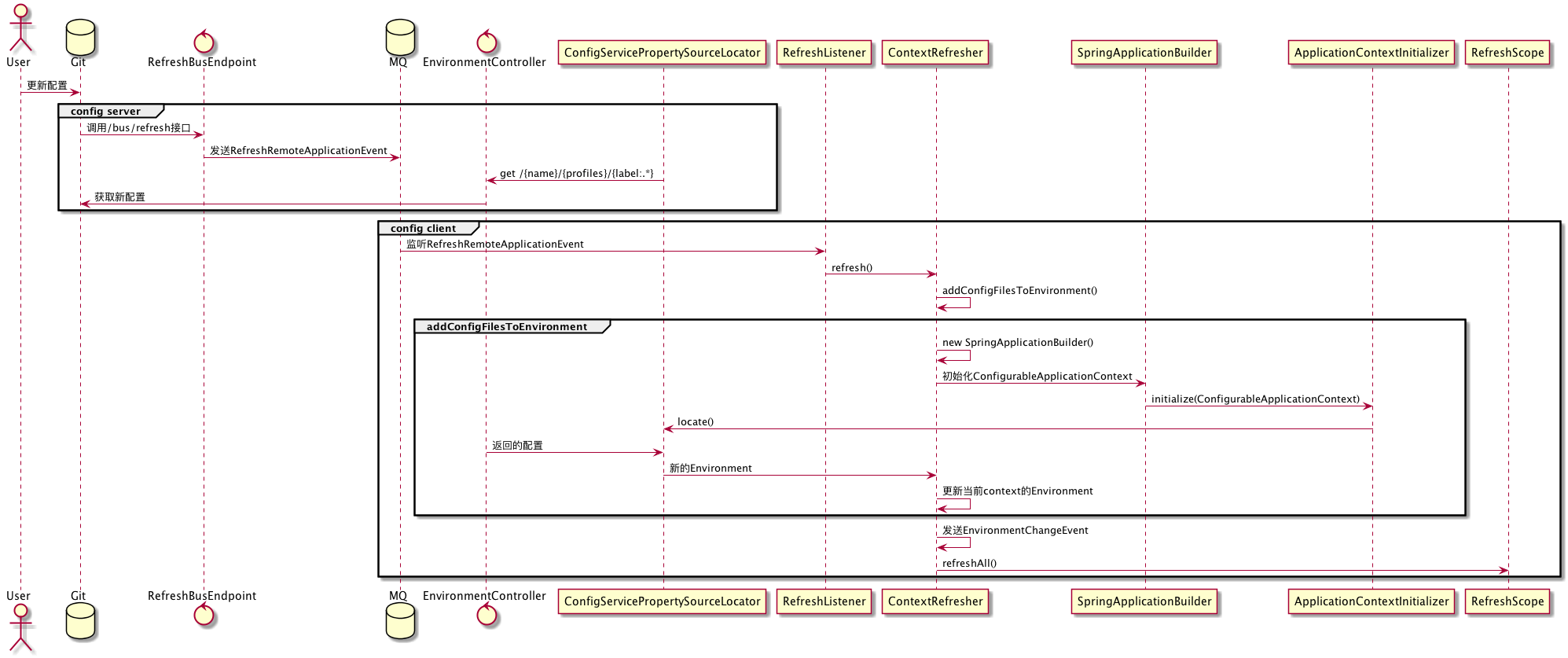
由上图可知当更新配置之后git会通过webhook调用/bus/refresh接口。 这是自动刷新配置的入口,代码如下:
@ManagedResource
public class RefreshBusEndpoint extends AbstractBusEndpoint {
//省略部分不重要代码
@RequestMapping(value = "refresh", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
@ManagedOperation
public void refresh(
@RequestParam(value = "destination", required = false) String destination) {
publish(new RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent(this, getInstanceId(), destination));
}
}
当调用了该接口时,会发送一个RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件。config server和config client都监听了该事件(也就是说config server也是可以刷新配置的)。
config client
事件的监听:
public class RefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent> {
//省略部分不重要代码
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent event) {
Set<String> keys = contextRefresher.refresh();
log.info("Received remote refresh request. Keys refreshed " + keys);
}
}
当发生RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件时会调用ContextRefresher的refresh()方法.该方法的主要内容如下
public synchronized Set<String> refresh() {
Map<String, Object> before = extract(
this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources());
addConfigFilesToEnvironment();
Set<String> keys = changes(before,
extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources())).keySet();
this.context.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(keys));
this.scope.refreshAll();
return keys;
}
- 从上下文指定的环境(对应profile)中的所有配置资源中提取配置(除了standardSources之外的配置)
private Set<String> standardSources = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList(StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
StandardServletEnvironment.JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
- 添加配置文件到Environment(这一步比较重要需要细聊,下一小结详解)
- 发送一个EnvironmentChangeEvent事件
- 刷新当前context的scope
添加配置到Environment的细节实现
ConfigurableApplicationContext addConfigFilesToEnvironment() {
ConfigurableApplicationContext capture = null;
try {
//拷贝环境
StandardEnvironment environment = copyEnvironment(
this.context.getEnvironment());
//1
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder(Empty.class)
.bannerMode(Mode.OFF).web(false).environment(environment);
// Just the listeners that affect the environment (e.g. excluding logging
// listener because it has side effects)
builder.application()
.setListeners(Arrays.asList(new BootstrapApplicationListener(),
new ConfigFileApplicationListener()));
capture = builder.run();
//2
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE)) {
environment.getPropertySources().remove(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE);
}
MutablePropertySources target = this.context.getEnvironment()
.getPropertySources();
String targetName = null;
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
String name = source.getName();
if (target.contains(name)) {
targetName = name;
}
if (!this.standardSources.contains(name)) {
if (target.contains(name)) {
target.replace(name, source);
}
else {
if (targetName != null) {
target.addAfter(targetName, source);
}
else {
// targetName was null so we are at the start of the list
target.addFirst(source);
targetName = name;
}
}
}
}
//3
}
finally {
ConfigurableApplicationContext closeable = capture;
while (closeable != null) {
try {
closeable.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore;
}
if (closeable.getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
closeable = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) closeable.getParent();
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
return capture;
}
- 拷贝环境(只是从main环境中拷贝默认配置源和profile)
从注释1到注释2之间发生了很有意思的事(实在不知道说什么好):
- 首先他会创建一个新的SpringApplicationBuild出来
- 然后通过build.run()方法创建一个新的ConfigurableApplicationContext出来
为何这么做呢?这又涉及到另外一个类:PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,先看下这个类实现的接口:
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered由于他实现了ApplicationContextInitializer
接口,所以当ConfigurableApplicationContext初始化时会调用它的public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext)方法: public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource( BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators); boolean empty = true; ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment(); for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators) { PropertySource<?> source = null; source = locator.locate(environment); if (source == null) { continue; } logger.info("Located property source: " + source); composite.addPropertySource(source); empty = false; } //省略部分代码 }最重要的一步是locator.locate(environment),该方法如下(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator类):
@Override @Retryable(interceptor = "configServerRetryInterceptor") public org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?> locate( org.springframework.core.env.Environment environment) { ConfigClientProperties properties = this.defaultProperties.override(environment); CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource("configService"); RestTemplate restTemplate = this.restTemplate == null ? getSecureRestTemplate(properties) : this.restTemplate; Exception error = null; String errorBody = null; logger.info("Fetching config from server at: " + properties.getRawUri()); try { String[] labels = new String[] { "" }; if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getLabel())) { labels = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(properties.getLabel()); } String state = ConfigClientStateHolder.getState(); // Try all the labels until one works for (String label : labels) { Environment result = getRemoteEnvironment(restTemplate, properties, label.trim(), state); //省略不重要的代码 }该方法主要是从远程获取Environment(其实际就是发送了个rest request到config server),因为该方法不允许失败,所以还添加@Retryable注解(在失败时重试) 1. 从注释2到3主要是将从远程获取的Environment和当前上下文的Environment做比较,当前Environment有的属性就替换,没有的就新增到当前的Environment中 1. 最后需要close掉新建出来的ConfigurableApplicationContext。
总结一下: config client为了能去远程获取Environment,创建了一个ConfigurableApplicationContext,用来触发ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator的locate方法,随后将新的配置更新到当前环境中,并关闭ConfigurableApplicationContext。
处理EnvironmentChangeEvent事件
ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder:
@Override public void onApplicationEvent(EnvironmentChangeEvent event) { rebind(); } @ManagedOperation public void rebind() { this.errors.clear(); for (String name : this.beans.getBeanNames()) { rebind(name); } } @ManagedOperation public boolean rebind(String name) { if (!this.beans.getBeanNames().contains(name)) { return false; } if (this.applicationContext != null) { try { Object bean = this.applicationContext.getBean(name); if (AopUtils.isCglibProxy(bean)) { bean = getTargetObject(bean); } this.binder.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, name); this.applicationContext.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() .initializeBean(bean, name); return true; } catch (RuntimeException e) { this.errors.put(name, e); throw e; } } return false; }
当发生EnvironmentChangeEvent事件时会重新初始化bean(包括重新绑定新的配置源以及重新校验metadata等,详情请查看spring core的官方文档)
scope刷新
RefreshScope:
public void refreshAll() {
super.destroy();
this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());
}
由于之前的bean重新初始化了,所以这里需要调用GenericScope的destroy().该方法会调用注册在BeanFactory中的bean destroy回调方法。
然后发送一个RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent事件。RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent事件的监听处理如下(EurekaDiscoveryClientConfiguration类):
@EventListener(RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent event) {
//This will force the creation of the EurkaClient bean if not already created
//to make sure the client will be reregistered after a refresh event
if(eurekaClient != null) {
eurekaClient.getApplications();
}
if (autoRegistration != null) {
// register in case meta data changed
this.autoRegistration.stop();
this.autoRegistration.start();
}
}
每当metadata发生变化就需要重新在eureka注册,实际上只要调用了/bus/refresh接口就会执行这一步骤。
由于调用了/bus/refresh接口就会触发RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件,并且config server和 config client都会监听该事件,而且该事件的处理是不管配置是否更新是否不是该微服务所需要的(即全量的)的都会执行scope的刷新 .所以只要你微服务使用了config的动态刷新,那么当任何一项配置更新时,你所有微服务都会在eureka中重新注册. 然后eureka的服务发现也是全量更新和读取的。然后你懂的。。。。。。